LAERA Classification
The first goal of document understanding is to identify the function and the meaning of a document and its parts. Typically a document is written for a specific purpose which defines its function. An invoice is designed and created to notify a buyer on the goods bought and how much money needs to paid for them, along with some other information for accounting and tax purposes. All content of the invoice follows this function. Or an application form in a bank is used to collect all information that is needed to open an account. This document is normally very structured. On the other side an e-Mail (which is also a document) conveys information, opens a discussion and calls for action in a very unstructured way.
So the first step in document understanding is to identify the function and separate the documents to be processed accordingly. Typically this step is called “Classification”. However this is only the primary classification or document type identification as more categorization according to a taxonomy can occur which do not have the purpose to define the function. It is therefore very important to distinguish these two types of classification as a lot of misunderstanding results from confusion between these. The function of a document determines the possible content and the information entities that can be found on it.
LAERA is easily integrated through activities in our platform VINNA or as Web API in a service container through TEGRA.
Learn more about classification in our detailed Articles on Classification from our blog archive.
LAERA Taxonomy
In a modern enterprise the distribution of tasks and the classification of documents follows a certain hierarchy that is often described as taxonomy. LAERA supports you in building the taxonomy as a hierarchical tree for classification. In fact the hierarchy that is obvious to the stake holders in a company often makes classification much more precise and easy to use. Hierarchical schemes can be used in sequence, in parallel or in any combination of both. LAERA allows you to define the main categories in general document input and then each department can add their own, more specific, subtypes to streamline their processes and automatically create decisions how to process a certain document.
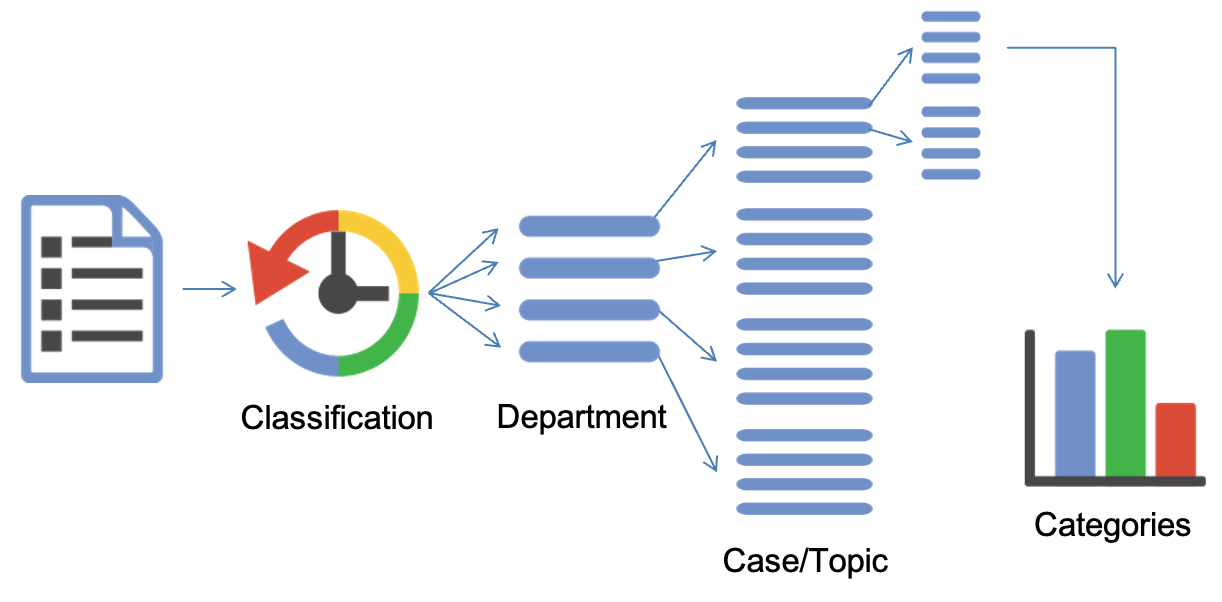
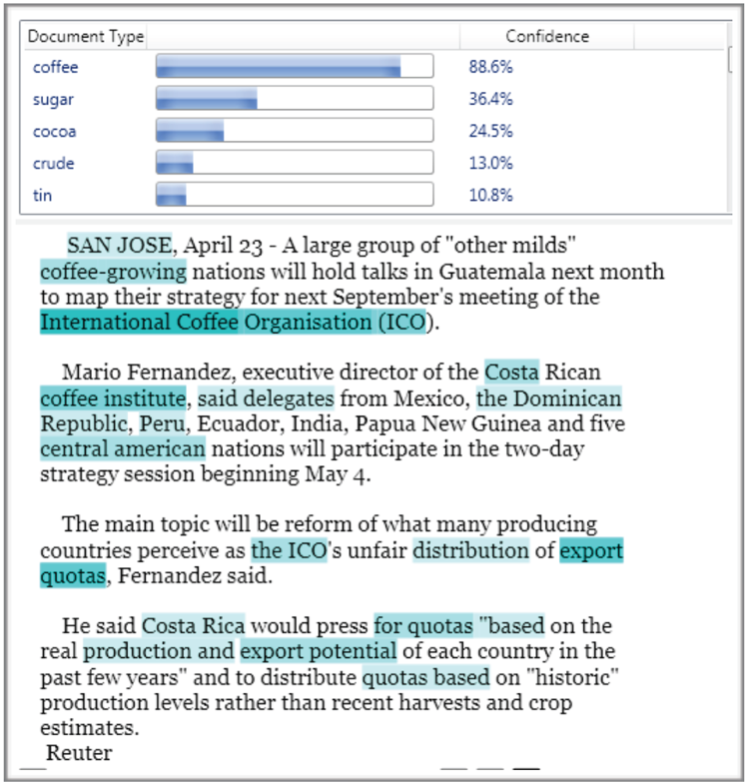
LAERA Content Classification
Information that is needed for processing documents and e-mails in an organization is hidden in unstructured formats. But computers can only understand structured data. Even after OCR conversion of a scanned document the meaning of the text is still not known to the backend system. This is where the Document Understanding becomes valuable because it allows assigning categories and topics to unstructured documents that allow mapping it to the formal structure of an enterprise process.
By putting the text into context with business organization and learned categories LAERA Classifier actually creates information. Content Classification is using trained features to determine the meaning of a document and assign it to a category. The relevant features, are automatically identified in the training process, using machine learning based on a representative number of sample documents for each category.
LAERA Content Classifier uses a combination of statistical classification methods that are ultra fast with modern international LLM (large language models) that can be enhanced with specific customer created rules to achieve the best possible results.
LAERA Clustering
Document Clustering is used to automatically detect categories in unsorted documents and suggest a taxonomy. Clustering is performed on images to identify similar layouts and on content to identify similar content. Clustering is used as a preparation step to prepare a training set for machine learning.
Benefits of Classification
- Computer programs use this information to automate processes
- Document management systems become structured, transparent and source of information
- Data becomes accessible to Business Analytic
- Automated decisions become possible
- People can be connected with relative content, because the topics and cases are known
- The risk of undiscovered critical information in archives is reduceds
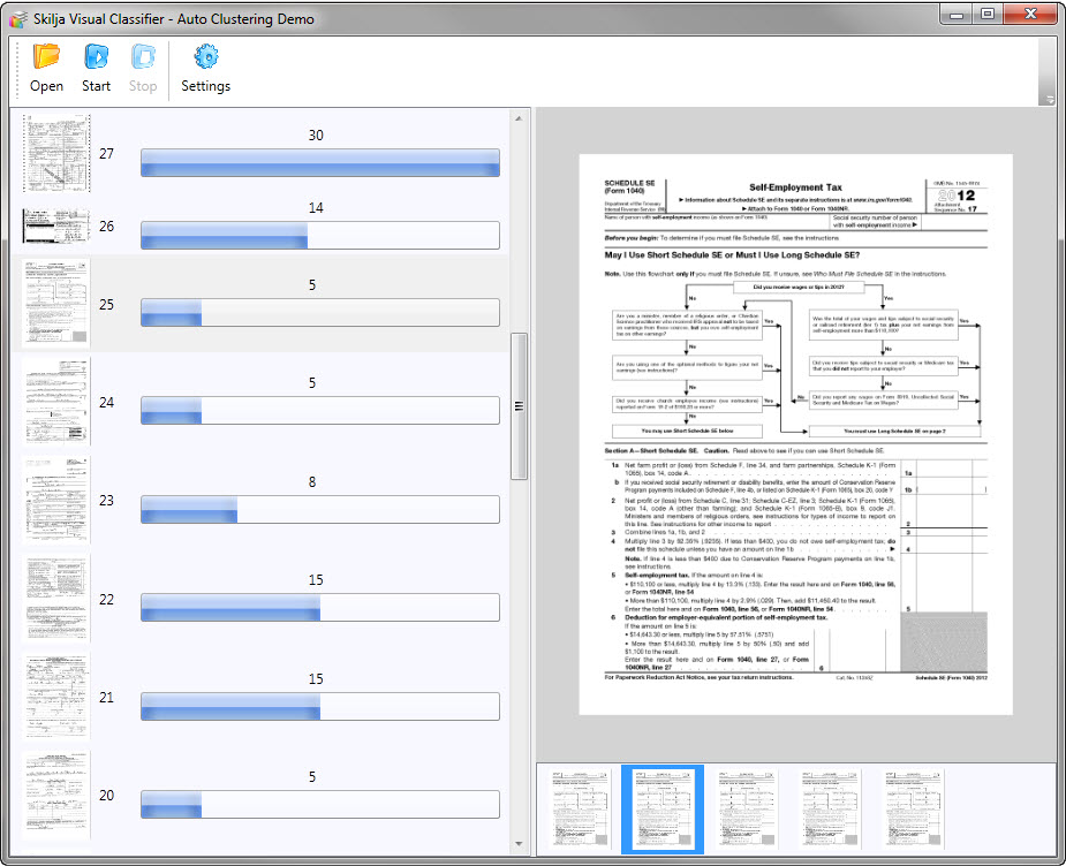

LAERA Document Separation
In Laera AI based classification document separation is built into a sequence of algorithms. Laera AI finds page locations automatically from the samples and hides this complexity from the users.
How does it work?
As usual in Laera all this is very fast and a separation of a stack of 200 pages with 150 document types takes less than 30 seconds in total. An introduction to document separation can be found here

LAERA Extraction
Once the document type is known from automatic or manual classification the document content can be analyzed and relevant information can be extracted. Laera Information Extractor uses a predictive generative approach to find and extract and validate relevant data from completely unstructured documents as e-Mails or contracts. Recognition of entities and fields is done in several steps where each possible value is analyzed and then assigned to its specific role (i.e. meaning) in the document. This works for totally unstructured free form documents as well as for logically structured documents like invoices and orders but also for traditional forms that can all be included in one extraction project without further configuration.
A number of articles and detailed descriptions on Information Extraction can be found in our blog: Articles on Extraction
LAERA Information Extraction
- Contracts (e.g. rental, insurance policies)
- Legal documents (e.g. deeds, affidavits, liens)
- Medical and Technical reports
- Invoices
- Forms
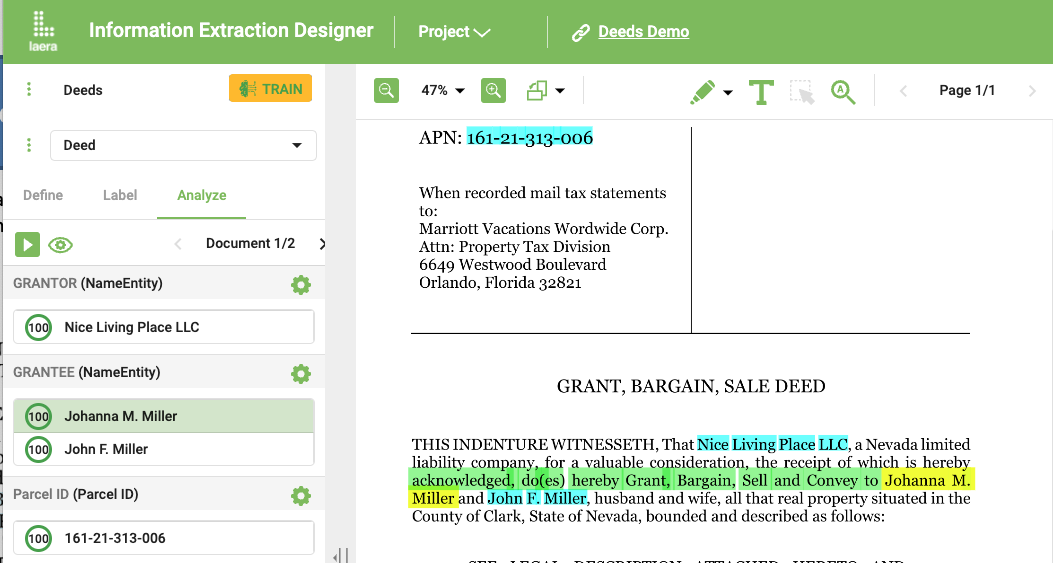
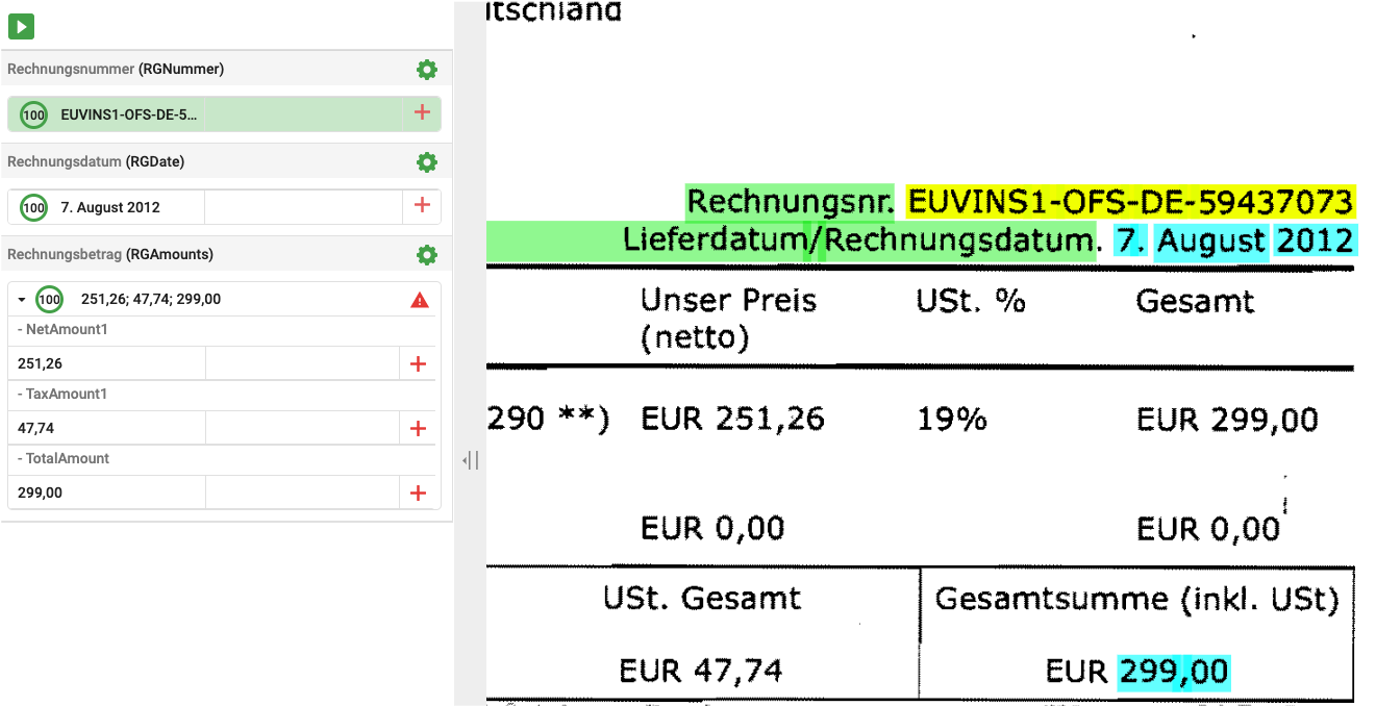
LAERA Invoice Recognition
As a special case for Extraction projects Laera offers a module for recognition of invoices. Extraction and Classification are pretrained and provide as knowledge bases that are binary and expose no private information. Recognition rates are high out of the box and are then further improved by additional training with customer documents.
Line items are detected and anayzed using the table recognition module which has specifically been optimized for invoice-type tables.
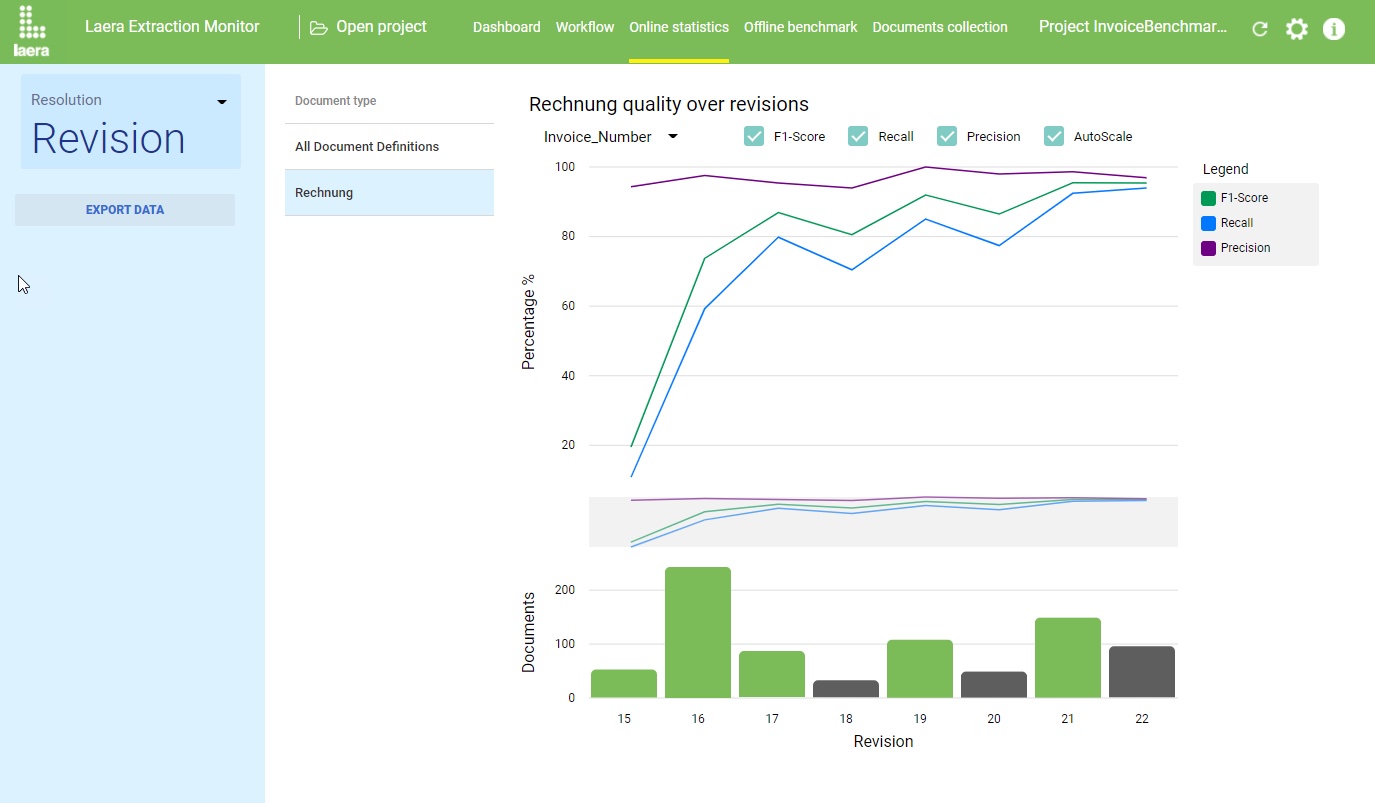
LAERA Online Learning
Classification and Extraction models can be continuously be improve with LAERA Online learning that runs as a service on premise in the background. No data needs to be sent to an external site. Online learning monitors the results from manual data correction and adds relevant new samples and features to the exiting model. This is done in a controlled way using revisions of the recognition project that are continuously tested and benchmarked in a background process. If the results improve the new model can be automatically or manually activated – with an immediate proven higher recognition rate. Revision by revision the system improves and and recognition rates in the high 90% range can be achieved without any further effort. Statistics monitor allow to control the quality day by day and down to single fields over time – giving full control to operations.